Reviewed by Anurag Mishra (Sr. Technical Consultant)
Laminar Air Flow (LAF) is extremely important in maintaining a contamination-free environment in industries and laboratories. LAF works by directing a steady, unidirectional flow of clean air to keep sensitive materials and equipment from airborne contaminants such as dust particles, etc.
Laminar Air Flow is used in microbiology, pharmaceuticals, and the manufacturing of electronics to ensure precision, sterility, and safety of products.
Laminar Air Flow is a controlled airflow system designed to eliminate any turbulence and contamination in products by ensuring
air flows uniformly in parallel layers. This type of airflow system eliminates contamination by maintaining a controlled environment, required for processes that demand high levels of cleanliness and sterility.
By delivering clean, controlled airflow, Laminar Air Flow systems are essential in ensuring the quality of sensitive operations, such as microbiological sample handling, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and accurate electronics assembly.
Laminar Air Flow is defined as a system that uses the unidirectional and consistent movement of filtered air at a uniform speed throughout a specified workspace to ensure minimal particle turbulence and sterility. Laminar Air Flow technology is the basis of contamination control in critical environments.
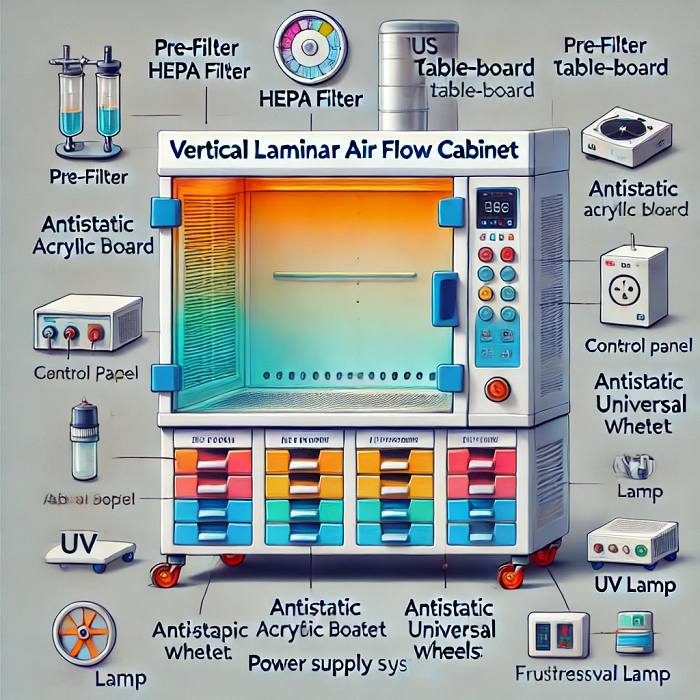
The Laminar Air Flow Diagram illustrates the structure and functioning of the LAF system. The Laminar Air Flow system is constructed of several key components:
The Pre-Filter is the first point of contact for air entering the Laminar Air Flow system. Its role is to trap larger particles like dust and lint, preventing them from reaching the sensitive HEPA filter, which extends the lifespan of the HEPA filter and enhances the efficiency of the LAF system.
The Blower Unit is powered by a motor that draws air into the system and pushes it through the filtration components. The constant flow generated by the blower ensures consistent airflow in the workspace.
The HEPA filter is the most essential component of the Laminar Air Flow system. HEPA filter captures 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns or larger, including dust, bacteria, etc. Placed after the pre-filter, the HEPA filter ensures that only clean, uncontaminated air enters the work area.
The plenum space is designed to evenly distribute the airflow before it passes through the HEPA filter. This helps maintain uniform flow and ensures that air moves consistently throughout the workspace.
The work surface is the clean platform where contamination-sensitive tasks are performed. It is located directly beneath the filtered air outflow. Work surface designed to remain free of airborne contaminants.
The UV light is installed inside Laminar Air Flow system to provide an additional layer of sterilization. When activated, it helps eliminate any remaining microorganisms in the workspace.
The control panel provides users with the ability to manage system settings, including airflow speed, lighting, and UV sterilization. It ensures easy operation and customization of the Laminar Air Flow unit.
The exhaust grill allows the controlled release of air from the LAF system, ensuring that no contaminants are released into the external environment. This maintains the quality of the sterile workspace.
The support frame provides structural stability to the Laminar Air Flow system. It holds all components in place and ensures durability during ongoing operations.
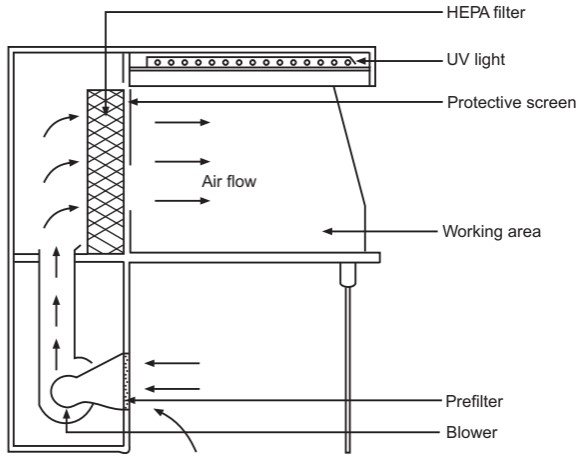
This Laminar Air Flow Pencil diagram shows how air is processed and distributed to create a contamination-free environment.
The principle of Laminar Air Flow revolves around the generation of a clean and controlled airflow. It ensures a contamination-free workspace by filtering air through pre-filters and HEPA filters, maintaining a steady airflow that prevents particle settlement and recirculation, making it ideal for sensitive operations.
Here is a detailed explanation of the working principle of the LAF system –
The working principle of the LAF system ensures that the workspace remains contamination-free from airborne particles, enabling contamination-sensitive tasks to be performed with accuracy.
Laminar Air Flow systems are essential in various applications due to their ability to maintain sterile and particle-free environments. Some applications of the Laminar Air Flow System are:
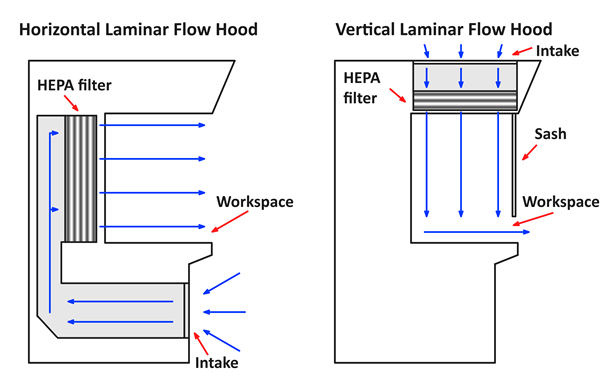
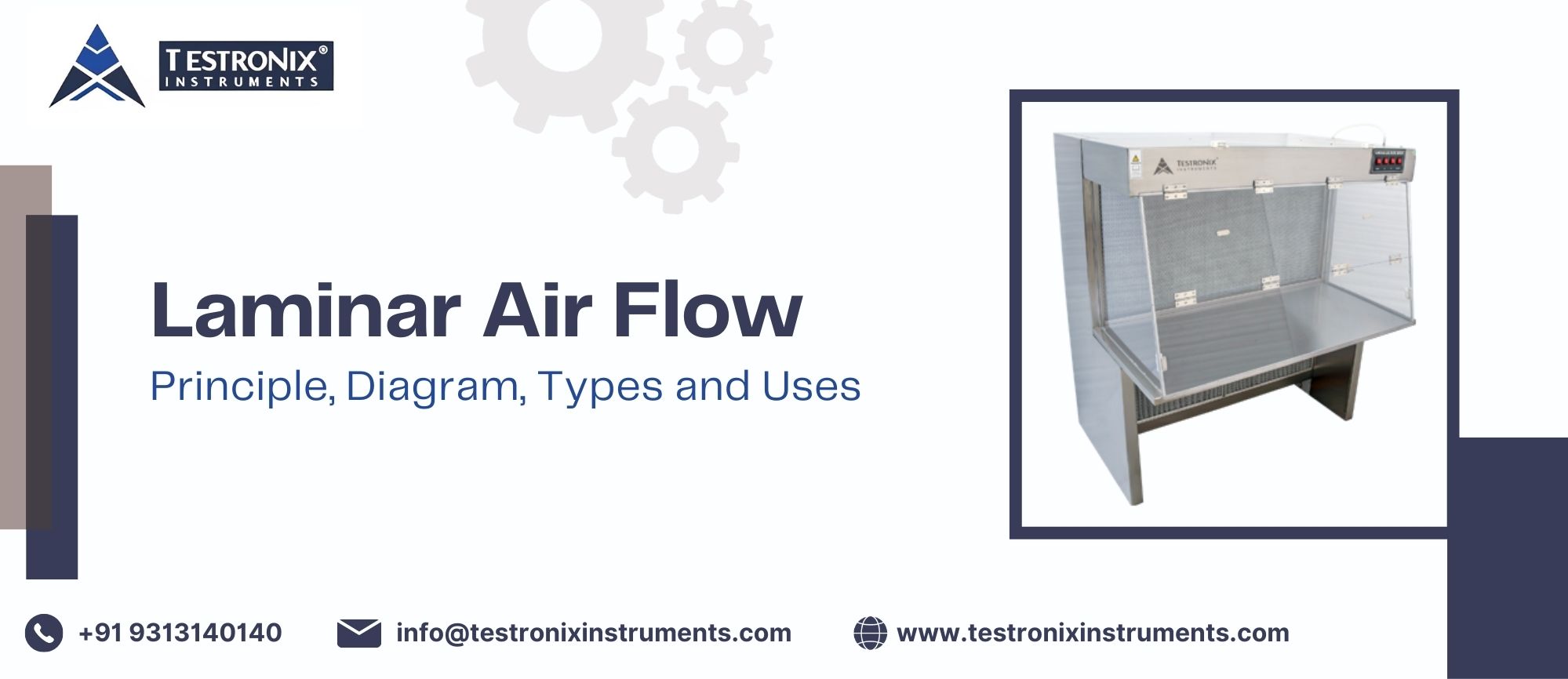
There are mainly 3 types of Laminar Air Flow systems based on the different types of airflow directions. Each type is suited for a specific application:
In Horizontal LAF, filtered air flows in the horizontal direction from the rear side toward the front. This ensures a clean airflow that sweeps across the work surface, preventing contaminants from settling.
Vertical LAF directs filtered air from the top of the unit to downward in a vertical pattern. The air flows uniformly across the work surface before exiting through the bottom or rear. This design effectively prevents contamination by pushing particles away from the workspace, making it useful in microbiology and pharmaceutical processes.
Reverse LAF systems are designed to pull air inward from the front of the unit to away from the operator and workspace. The air is filtered and directed toward an exhaust, effectively containing and removing hazardous particles or contaminants.
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filter is a necessary component of Laminar Air Flow systems. It removes 99.97% of particles ≥0.3 microns, including dust, bacteria, etc. ensuring the air entering the workspace is contaminant-free. HEPA filters are essential for maintaining ISO cleanroom standards and providing a sterile working environment.
Laminar Air Flow (LAF) is a controlled airflow system that eliminates turbulence and contamination by ensuring clean air flows uniformly in parallel layers. It maintains a sterile and particle-free environment necessary for sensitive operations.
Applications of Laminar Air Flow include:
Laminar Air Flow work as:
Laminar Air Flow has a variety of applications. Here are some real life applications of laminar flow:
Laminar Flow is important for: