Reviewed by Anurag Mishra (Sr. Technical Consultant)
The measurement of melt flow properties is a critical aspect in the characterization of polymers, providing valuable insights into their processing behaviour and end-use applications.
At the forefront of this analysis is the melt flow index (MFI) tester, a high-quality lab testing instrument designed to quantify the flow ability of molten polymers under specific conditions.
This MFI tester operates on a principle that involves extruding a standardized amount of polymer through a precisely calibrated capillary under controlled temperature and pressure conditions. In this blog, we will focus on how you can easily measure the melt flow properties of polymers. So, let us get started!
Melt flow index (MFI) testing is a widely embraced technique within the plastics industry, serving as a crucial method for assessing the viscosity and flow properties of polymer melts.
This pivotal test holds significance in enabling manufacturers to gain comprehensive insights into the behaviour of their plastic materials throughout the processing stage and in their ultimate performance in end-use applications. The primary objective of conducting melt flow index testing is to precisely quantify the fluidity and viscosity characteristics inherent in polymers.
This information becomes instrumental for manufacturers in evaluating the suitability of their materials for specific manufacturing processes and verifying compliance with stringent quality standards.
Notably, different manufacturing processes may necessitate materials with varying melt flow indexes, thereby emphasizing the versatility of this testing methodology. Additionally, by scrutinizing the melt flow index of plastic resins before their transformation into final products, manufacturers can uphold a consistent and high-quality production process.
In the realm of plastics and materials science, the term "polymer" is frequently encountered, but what exactly does it signify? In straightforward terms, a polymer constitutes a large molecule constructed from recurring units known as monomers. These monomers intricately link together, forming extended chains and giving rise to the structure of a polymer.

Polymers manifest in diverse forms, spanning the realms of both natural and synthetic materials. Examples of natural polymers encompass rubber, silk, and cellulose, while synthetic polymers, such as those found in everyday items like plastic bottles, bags, and packaging materials, are crafted through human ingenuity.
Having defined the nature of polymers, it's pertinent to explore the significance of melt flow properties in comprehending these materials. Melt flow properties elucidate a polymer's ability to flow when subjected to heat, a critical attribute that profoundly influences the quality and uniformity of products manufactured from these materials.
The widely employed melt flow index (MFI) test serves as a key method for gauging this property. The process involves the controlled heating of a small quantity of polymer resin until it reaches its melting point, followed by its passage through a standardized orifice under constant pressure. The ensuing measurement of the molten polymer's flow rate through the orifice is recorded as its melt flow rate (MFR) or melt index (MI).
Now, let us discuss some easy-to-follow steps to measure the melt flow properties of polymers.
You can easily measure the MFI properties of polymers by following the steps mentioned below:
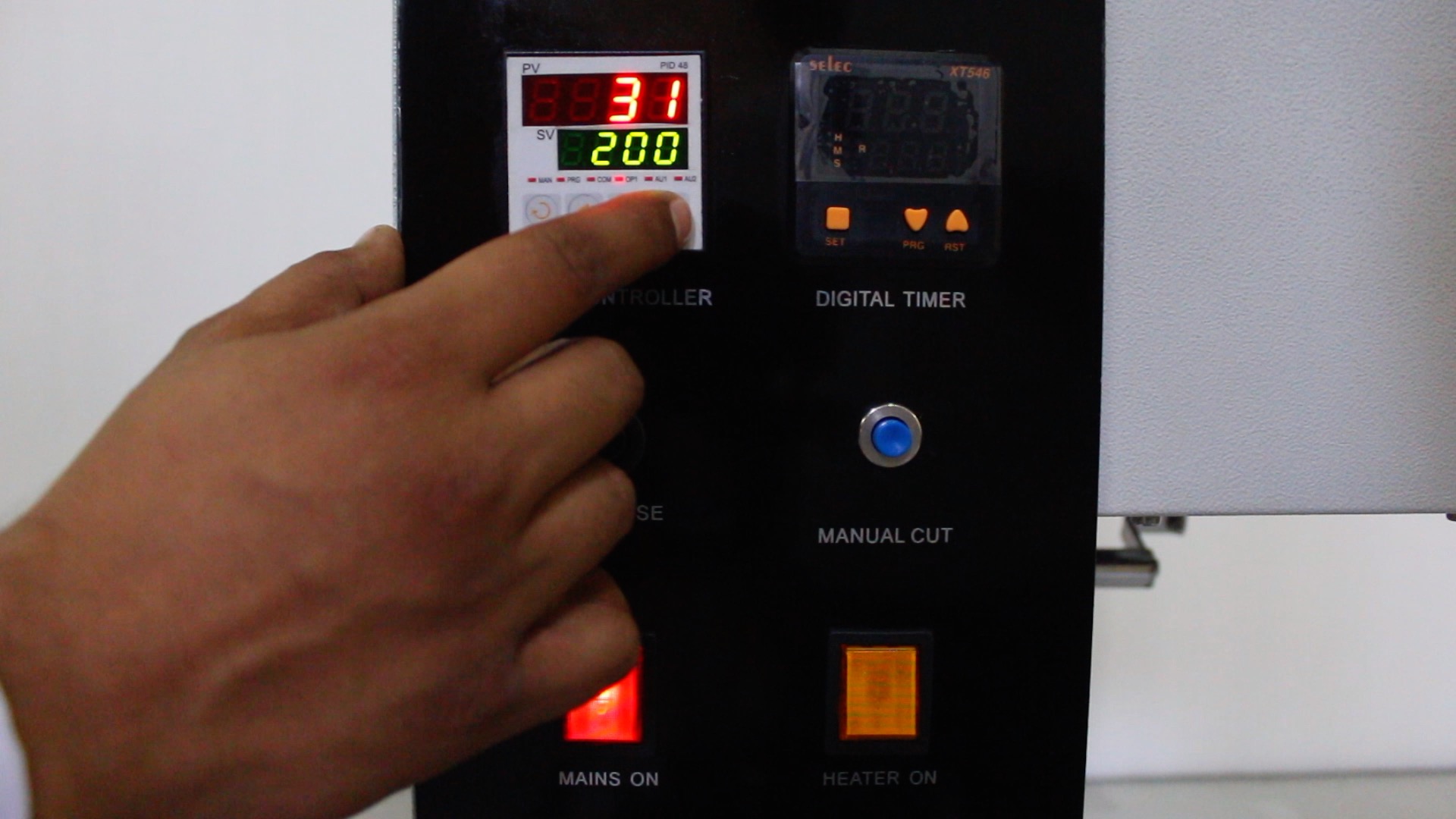
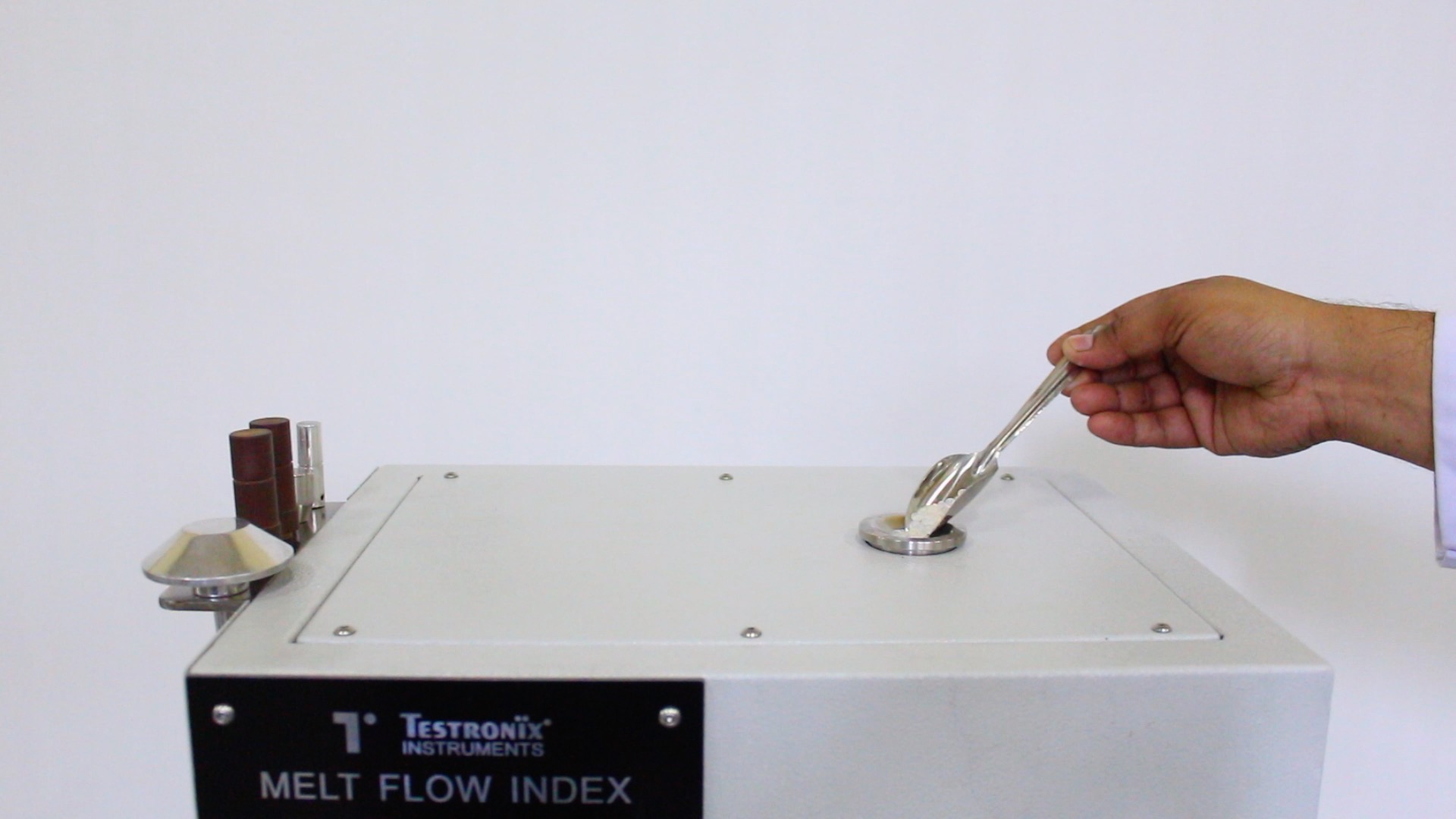


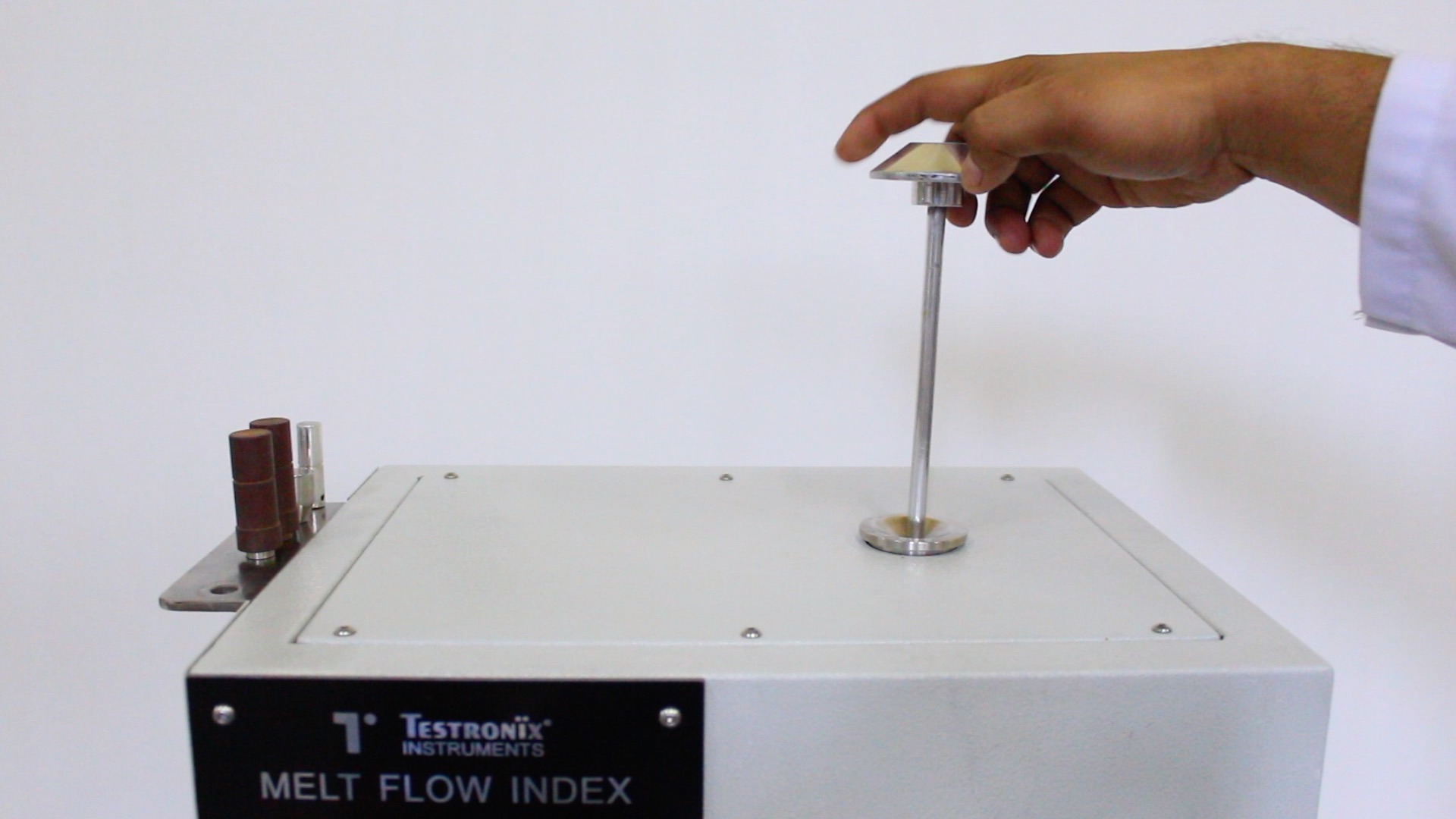
Calculate the MFI using the formula:
MFI = Weight of sample in gm/ 10 min.
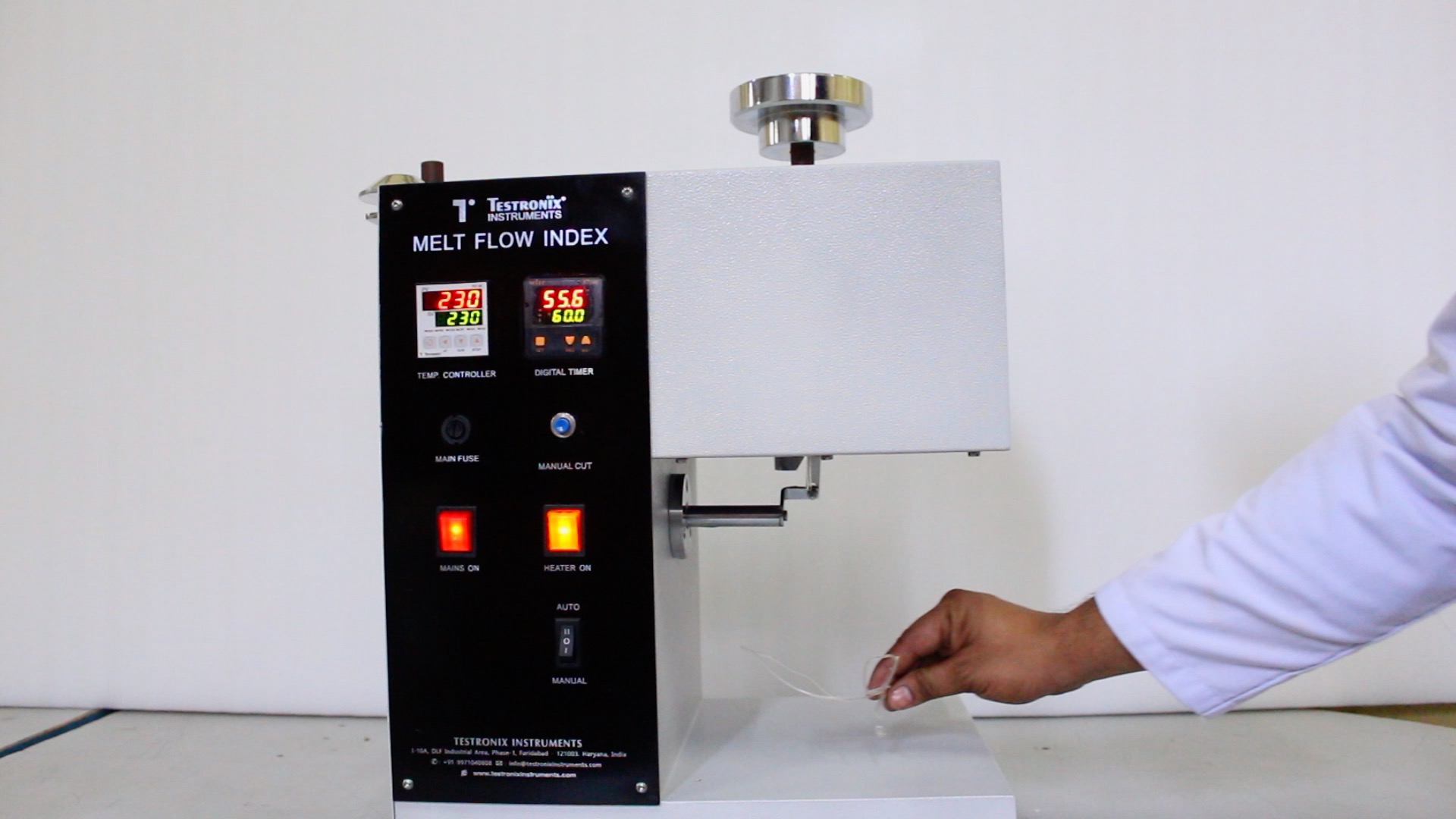

In this way, you can easily conduct melt flow index tests on the materials and ensure that accurate products will be delivered to the customers. If you want to know more about this testing instrument, then you can give us a call at +91 9313 140 140 or email us at info@testronixinstruments.com. Our team of experts will consult you regarding all your needs and queries.